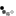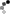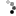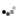dB, db, is short for decibel, dB = 10lgX, it is purely a statistical unit of multiple and amplitude, which has three advantages, the data is small and easy to read, the other is easy for addition and subtraction operation, the third is easy to estimate.
For example,
if the multiple X = 100000 = 10^5
then X(dB) = 10*lg(X) dB= 10*lg(10^5) dB= 50 dB
if the amplitude X = 0.000000000000001 = 10^-15
then X(dB) = 10*log(X) dB= 10*log(10^-15) dB= -150 dB
The data of db is smaller than the multiple and amplitude, which is easier for reading, addition and subtraction.
In the field of electronics, there is a bit difference among the voltage, current, power amplitude.
For example,
the db of voltage amplitude is A(V)(dB)=20lg(Vo/Vi)
the db of current amplitude is A(I)(dB)=20lg(Io/Ii)
the db of power amplitude is Ap(dB)=10lg(Po/Pi)
Please see the attachment of coordinates about the voltage/current and power amplitude!
There are special points on the coordinates, (1. 0), (2. 3), (1/2. -3), (1.414. 3), (0.707. -3).
10lg1=0dB, 10lg2=20lg1.414=3dB, 10lg1/2=20lg0.707=-3dB